Bradley Little, a physical education teacher in Arizona, was leading his class through a school hallway in 2017 when he collapsed. Little feared he was having a stroke. Or, in a sign of the times, that he’d been shot. He tried to stand, but his leg wouldn’t move.
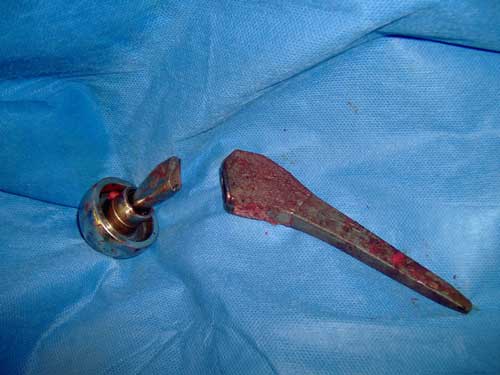
A student ran for help. Firefighters arrived and hoisted Little onto a gurney. At the hospital, an X-ray revealed that the artificial hip implant in Little’s right leg had “suddenly and catastrophically structurally failed,” according to a lawsuit Little would later file in federal court. The implant severed at its “neck” — a 2-inch-long titanium part linking Little’s thigh to his torso.
“It looked like a laser went through it,” Little said in an interview. “It was like someone just went in there and cut it right in the middle.”
Profemur artificial hips were once considered innovative for a feature known as “dual modular necks,” intended to modernize total hip replacement surgery. Hundreds of thousands of Americans undergo hip implant surgery each year and devices are expected to last at least 20 years, according to the American College of Rheumatology. The Profemur necks, available in an array of lengths and angles, made it easier to customize the hip implants for patients.
But the neck also proved to be a weak point: Over the past two decades, more than 750 Profemur hips like Little’s have fractured at the neck, an attorney for the manufacturer has said in court. In interviews, patients said they were left unable to walk and in need of emergency surgery. Reports submitted to the FDA describe Profemur patients stranded in the midst of routine life, while hiking, golfing, bowling, mowing the lawn, lifting a potted plant, getting out of a chair, putting on pants, and leaning over to pick up a key.
After each break, patients endure an hours-long repair surgery that can be traumatic because the broken implant is embedded in their bone and difficult to remove, according to three orthopedic surgeons who’ve performed such a procedure. The repair surgery, which can cost tens of thousands of dollars and may not be fully reimbursed by insurance, often requires a patient’s femur to be cracked open to extract a metal stem that was inserted down its length. Lawsuits have likened removing the bone around the stem to peeling a banana.
Read more at CBSnews.com